Support of wireline access network
The architecture for non-roaming is shown in figure
1, where the Wireline Access Gateway Function (W-AGF) is the access node performing
the termination of N2 and N3 reference point, termination of access network
interface Y4 and all access network specify functionalities, the relay of N1
to/from the UE., QoS enforcement, etc. The customer device, the UE, is replaced
by the Residential Gateway which is augmented to support the 5G functionalities
required to connect to 5G systems, such as NAS, URSP, PDU session, etc, called
5G-RG. The specification in TS 23.316 defines the modification to system
architecture, procedure and flows, Policy and Charging Control for the 5G
System in TS 23.501, TS 23.502 and TS 23.503.
The 5G-RG can also be connected via 3GPP Access
basically by means of supporting the specification defined for UE. This
scenario is called Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). Furthermore the 5G-RG may
simultaneously connect to 3GPP Access and to wireline access by using the
Single Access PDU session or supporting ATSSS feature. This scenario is called
Hybrid scenario, using a terminology common on wireline access network. The
ATSSS is supported as specified in TS 23.501, 23.502 and TS 23.503 where UE is
replaced by 5G-RG and the Non-3GPP access is specifically referred to
wireline access. In this latter case, TS 23.316 has also specified the support
of interworking with EPC via 3GPP Access via a MA PDU session with a PDN
Connection as user-plane resource associated with a MA PDU Session.
The support of legacy Residential Gateway not
supporting 5G capability (FN-RG) is supported via W-AGF terminating the N1 NAS
on behalf of UE and acting as a UE in respect the 5G core.
In the case of Wireline Access Network defined in
Broadband Forum the W-AGF functionalities is specified in BBF TR-470, BBF
TR-456 and BBF TR-457, the 5G-RG is defined in BBF TR-124issue6 [8]. In
the case of Wireline Access network defined in Cablelabs the W-AGF and 5G-RG
functionalities are defined in CableLabs WR-TR-5WWC-ARCH.
Main impacts on the system by the WWC for wireline support are the following:
- W-AGF: the access network
function which performs the termination of N2 and N3 reference point,
termination of access network interface Y4 and all access network specify
functionalities, the relay of N1 to/from the UE. QoS enforcement, etc. When the
W-AGF facing the FN-RG the W-AGF is supporting the termination of N1 NAS and
performs the interworking between 5GC and the legacy wireline access network.
- 5G-RG: end user device
replacing the UE which supports 5G capabilities (NAS protocol and procedure,
USRP, IMSI, ATSSS) and extension of wireline access layer specific
functionalities defined by Broadband forum and CableLabs. The 5G-RG may also
support UE capability when connects via 3GPP Access.
- FN-RG: end user device
replacing the UE which does not support 5G capabilities.
- Global Line Identifier (GLI):
in case of wireline access based on BBF specifications this parameter uniquely
identifies the line at which the 5G-RG in connected to within an operator
domain.
- Global Cable identifier (GCI):
in case of wireline access based on CableLabs specification this parameter
uniquely identifies the line at which the 5G-RG in connected to within an
operator domain.
- SUPI for FN-RG based on GCI
and GLI.
- All procedures defined in TS
23.502 have been modified to introduce the new network elements. The procedures
are focused mainly on the part of specification that required improvements and
to point out the access network interaction involving the W-AGF, 5G-RG and
FN-RG to allow the Broadband Forum and CableLabs to develop the specifications
under their responsibility.
- IPTV support: The
specification TS 23.316 in clauses 4.9.1 and 7.7.1 defines the support of IPTV
via the support of multicast over unicast PDU session by using IGMP/MLD message
send by STB via 5G-RG on PDU session and managed by UPF for adding the
requiring 5G-RG to a multicast group and replicating the traffic received on N6
interface to the PDU session. The SMF is improved to control the support of
IPTV by the UPF acting as PSA using PDR, FAR, QER, URR. This includes control
of which IGMP and MLD requests the UPF is to accept or to deny.
- QoS: the QoS model for
wireline network is based on a subscription maximum aggregate bitrate including
both GBR and Non-GBR traffic, hence the new parameter RG Total Maximum Bit Rate
(RG-TMBR) has been defined. The RG-TMBR limits the aggregate bit rate that can
be expected to be provided across all GBR and Non-GBR QoS Flows of a RG. The
RG-TMBR is a parameter provided to the W-AGF by the AMF based on the value of
the Subscribed RG-TMBR retrieved from UDM. The QoS control on wireline access
network (i.e scheduling, rate limiting and traffic class management) is based
on the line characteristic included in user subscription, for example different
priority of service, different traffic class support by line of the single
user, etc, for such reason the new parameter RG Level Wireline Access
Characteristics (RG-LWAC) has been introduced. The format and content of RG
LWAC is specified by BBF and it is transparently provided by UDM to AMF which may provide to the W-AGF at the time of the RG registration
- mobility restriction based on
GLI and GCI
- support of BBF interaction
with the Access Configuration System (ACS) to support the provisioning of
configuration and remote management of 5G-RG as described in BBF TR-069 [12] or
in BBF TR-369.
 |
| Non- roaming architecture for 5G Core Network for 5G-RG with Wireline 5G Access network and NG RAN |
 |
| Non- roaming architecture for 5G Core Network for FN-RG with Wireline 5G Access network and NG RAN |
Support of Trusted Access network
The support of Trusted Network addresses the
scenario where the Non-3GPP access network has a tighter relationship with 5GC
in respect the untrusted scenario. However how the network is considered
Trusted or Untrusted is not in the scope of this WID. The architecture for
non-roaming is shown in figure 3, where the Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network
(TNAN) is the access node performing the termination of N2 and N3 reference
point, termination of access network interface, relay of N1 to/from the UE.
From 3GPP point of view the TNAN network is composed by the TNGF and the
Trusted Non-3GPP Access Point (TNAP) which are interconnected via the reference
point Ta. However the detailed definition of TNAN and of Ta is beyond the WID
scope. The reference point between the UE and the TNG, the NWt, is specified
leveraging the IKEv2 defined for Untrusted. The main difference in contrast to
Untrusted is in registration procedure, where it is assumed that EAP-5G can be
carried between UE and TNAP directly on access layers, such on IEEE 802.11x and
between TNAP and TNGF via Ta and not as part of IKEv2 establishment. From other the point of view of other
procedures, such as session management, the same procedure specified for
Untrusted Non-3GPP access network can be used with basically the TNGF replacing
the N3IWF, and modification that IKEv2 Child SA establishment is requested by
TNGF and not by UE side.
Within the context of Trusted Non-3GP network, also
the scenario of devices not supporting NAS connected via WLAN is specified. The
role of TNGF is replaced the Trusted WLAN Interworking Function (TWIF) with the
main difference that TWIF terminates the N1 NAS interface and it play the role
of UE in respect the 5GC.
The specification is addressed in TS 23.501, TS
23.502 and TS 23.503
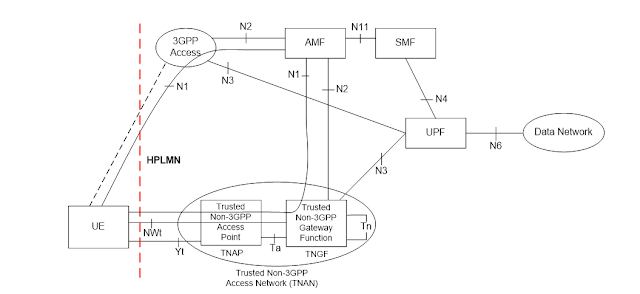 |
| Non-roaming architecture for 5G Core Network with trusted non-3GPP access |
Radio aspects
The objective includes:
• The
description and enhancement of NG protocols to support the interface between
the Trusted Non-3GPP Access Network and the 5GC;
• The
description and enhancement of NG protocols to support the interface between
the Wireline 5G Access Network and the 5GC.
- from TS 29.413 and TS 38.413.
General radio aspects
- Introduce
the Trusted Non-3GPP Gateway Function (TNGF), Trusted WLAN Interworking
Function (TWIF) to support the Trusted Non-3GPP Access, and Wireline Access
Gateway Function (W-AGF) to support Wireline Access in TS 29.413 and TS 38.413.
- Add the
Global TNGF ID in the applicable NGAP messages between the TNGF and the AMF;
add the Global TWIF ID in the applicable NGAP messages between the TWIF and the
AMF; add the Global W-AGF ID in the applicable NGAP messages between the W-AGF
and the AMF.
- Add the
selected PLMN Identity for trusted non-3GPP access and wireline access in Initial
UE Message for Key derivation.
- Add
procedural texts that the Security Key IE may include KTNGF, or KTWIF, or KWAGF
in TS 29.413.
Supporting the Trusted Non-3GPP Access
with the 5GC – specific aspects
- Add TNGF
Identity Information, TWIF Identity Information in the UPLINK NAS TRANSPORT
message containing a list of identifiers of NG-U terminations at TNGF/TWIF for
UPF selection.
- Add TNGF
related and TWIF related User Location Information in the User Location
Information IE.
Supporting the Wireline Access
connectivity with the 5GC – specific aspects
- Add
W-AGF Identity Information in the UPLINK NAS TRANSPORT message containing a
list of identifiers of NG-U terminations at W-AGF for UPF selection.
- Add
W-AGF related User Location Information in the User Location Information IE.
- Add
procedural texts to clarify the UE-AMBR is not used for wireline access in TS
29.413.
- Add RG
Level Wireline Access Characteristics in INITIAL CONTEXT SETUP REQUEST messages
stored in the UE context by the W-AGF, indicating the wireline access
technology specific QoS information corresponding to a specific wireline access
subscription.
- Add the
Authenticated Indication in INITIAL UE MESSAGE to indicate that the FN-RG has
been authenticated by the wireline 5G access network.
Charging
aspects
The Wireless and Wireline Convergence for 5G system architecture (5WWC)is specified in TS 23.501, TS 23.502, TS
23.503 and TS 23.316. The enhancement to charging aspect for 5WWC is considered
as part of this series specifications for this 5WWC.
Following
charging scenarios are included in charging aspect of 5WWC as following:
- UE Connects to 5G Core via Trusted Non-3GPP
access
- 5G-RG connects to 5G Core via NR-RAN and via
W-5GAN
- FN-RG connects via W-5GAN.
The
specifications related to 5WWC charging include TS 32.255, TS 32.291 and TS
32.298. The subscriber’s identifiers and PEI in 5G-RG and FN RG scenarios
specified in TS 23.501 and TS 23.361 are used in charging information. The
procedures and related triggers in 5WWC charging scenarios are also specified
in charging aspect for 5WWC. The related changes to OpenAPI are specified in TS
32.291.










