2-step RACH for NR
The Rel-16 2-step RACH for NR achieves the following objectives:
- A simplified random access
procedure was developed. This reduces the number of interactions between the UE
and network during the connection setup and connection resume, thereby enabling
a lower control plane latency. In case of connected mode, a small amount of
data can be sent via 2-step RACH procedure thus also enabling a lower latency
for UL UP data for connected mode UEs.
- Channel structure of transmitting
PRACH and PUSCH in one step (i.e. without an intermediate message from the
network) was developed. The PRACH and PUSCH are separated by a pre-configured
guard period.
- The above enhancements are applicable to both licensed spectrum and shared spectrum (i.e. NR-U).
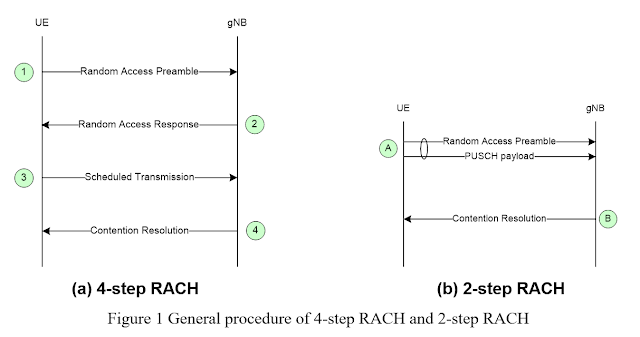
The
general procedure of 4-step RACH and 2-step RACH are depicted in Figure 1. The first
step of 2-step RACH comprises an UL MSGA transmission which includes the
equivalent contents of msg1 and msg3 of 4-step RACH. The second step of 2-step
RACH is a DL MSGB reception which includes the equivalent content of msg2
and/or msg4 of 4-step RACH, depending on the detection of UL MSGA.
RA type
selection
For
contention based random access (CBRA), all the triggers for Rel-15 NR 4-step
RACH are also applicable to 2-step RACH except when CA is configured, the
2-step RACH is only applicable on PCell. Contention free random access (CFRA)
procedure with 2-step RACH is only supported for handover.
The UE
selects the type of random access at initiation of the random access procedure
based on network configuration:
- when CFRA resources are not
configured, an RSRP threshold is used by the UE to select between 2-step RA
type and 4-step RA type;
- when CFRA resources for 4-step RA
type are configured, UE performs random access with 4-step RA type;
- when CFRA resources for 2-step RA
type are configured, UE performs random access with 2-step RA type.
In case
of random access in a cell configured with SUL, UE performs carrier selection
(between SUL and NUL) before selecting between 2-step and 4-step RA type.
MSGA
structure: PRACH
The MSGA
in 2-step RACH comprise a PRACH and a PUSCH. The PRACH resources for 2-step
RACH in time/frequency domain can be either shared with 4-step RACH or can be
configured to be separate. All the preamble formats and the PRACH configuration
indexes defined in Rel-15 and in Rel-16 NR-U and TEI can be used. In case of
shared time domain PRACH resources between 4-step RACH and 2-step RACH,
different preambles are allocated to differentiate the RA types. The mapping between SSB and PRACH occasion
reuses that for 4-step RACH.
MSGA
structure: PUSCH
2-step
RACH uses a specified mapping rule to determine the PUSCH resource of MSGA that
is associated with the selected PRACH resource. Each PRACH slot is mapped to a
number of PUSCH occasions with associated DMRS resource, once the UE selects a
preamble in a PRACH occasion, the corresponding PUSCH occasion and DMRS
resource can be determined by a predefined mapping order.
MSGB
After
MSGA transmission, the UE monitors the downlink for a response from the network
within a configured window. This response from the network is called the MSGB.
The contents of MSGB depend on whether or not the gNB is able to successfully
detect both the PRACH and the PUSCH parts.
- If the PRACH is detected but the
decoding of PUSCH fails, network will include a fallback indication in MSGB and
the subsequent UE procedure will be similar to that for a UE monitoring msg2 in
the 4 step RACH.
- If both preamble and PUSCH are
decoded, network will include a successRAR and reception of this at the UE
completes the contention resolution. HARQ feedback is enabled for the
successful reception of the successRAR.
References
[1] RP-200085, Revised WID
on 2 step RACH for NR
[2] RP-200622, Status report
for WI - NR 2-step RACH
0 comments:
Post a Comment